PORTE´S FIVE FORCES (tool)
Brief description
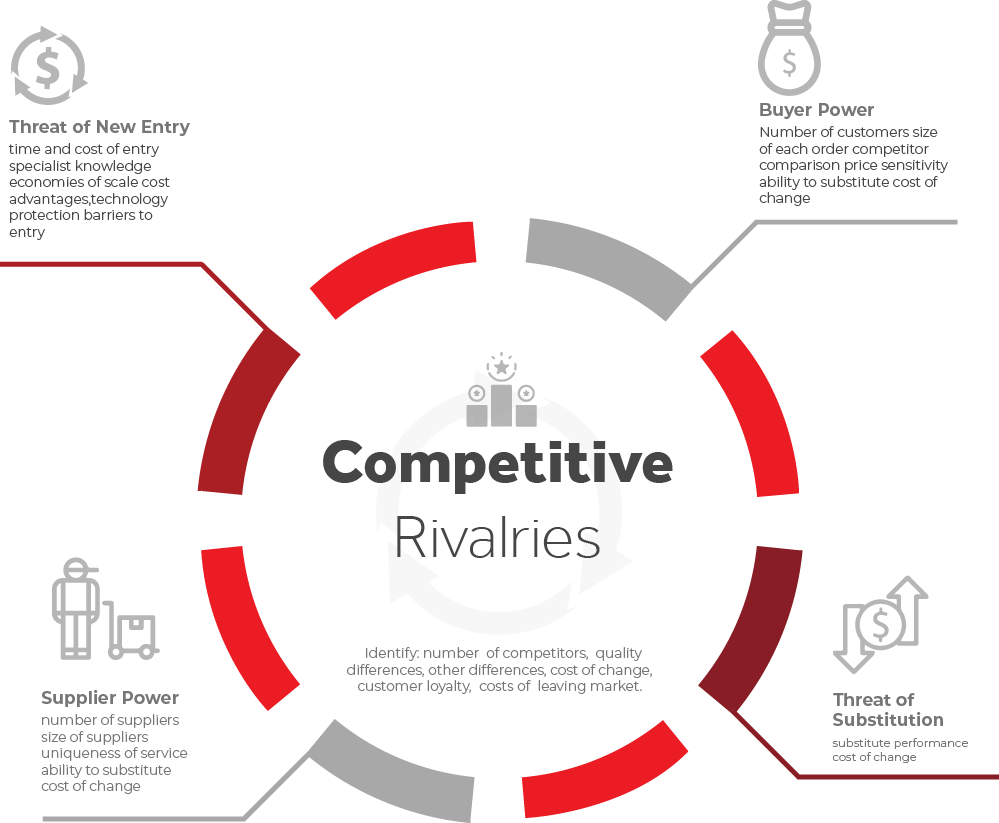
Effective for understanding the competitive intensity of an industry. The five forces include: the threat of potential entrants to the market, the threat of substitute products or services, the trading power of customers, the trading power of suppliers, and the intensity of rivalry among competitors.